Fuzzy Logic |
| It is a computational technique that is based on how humans think. For example, a human may conclude that a room is hot without knowing the exact temperature value. Consequently, a human may turn on a fan when the room is hot. In other words, the human brain can use vague information to make decisions and fuzzy logic is trying to simulate this behavior of the human brain. In other words, fuzzy logic is a method for reasoning using logical expressions that considers "degrees of truth" instead of the classic terms "true" or "false". Es una técnica computacional que está basada en cómo los humanos piensan. Por ejemplo, un humano puede concluir que un cuarto está caliente sin conocer el valor exacto de la temperatura. Consecuentemente, un humano puede encender un ventilador si el cuarto está caliente. En otras palabras, el cerebro humano puede usar información vaga para tomar decisiones y lógica difusa trata de simular este comportamiento del cerebro humano. En otras palabras, la lógica difusa es un método para razonar usando expresiones lógicas que considera los "grados de verdad" en lugar de los términos clásicos "verdad" o "falso". |
Fuzzy Set |
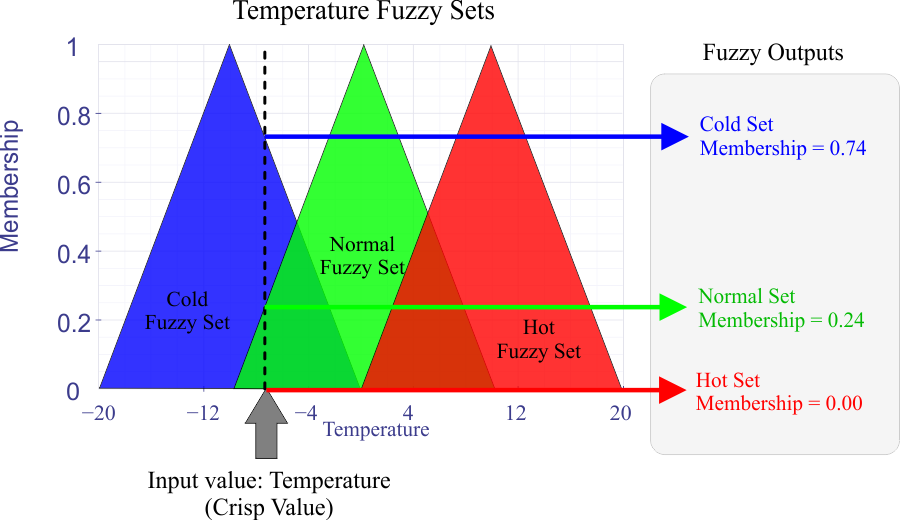
| A fuzzy set is used to convert a crisp value to a fuzzy value. Suppose you have a fuzzy set called "Hot" to represent the temperature in room. If the temperature is the crisp value, the membership to the "Hot" fuzzy set is a number from 0 to 1 that represents the degree of "Hot". For example, if the temperature is 95 F, then the membership to the "Hot" fuzzy set must be very close to one. On the other hand, if the temperature is -20 F, then the membership to the "Hot" fuzzy set must be zero. Thus, the fuzzy value represents how "Hot" is the room. Some functions that are used to create fuzzy sets are: triangle, trapezoid, Gaussian, etc. Un conjunto difuso es usado para convertir un valor nítido a un valor difuso. Suponga que usted tiene un conjunto difuso llamado "Caliente" para representar la temperatura de un cuarto. Si la temperatura es un valor nítido, el valor de membrecía al conjunto difuso "Caliente" es un número de 0 a 1 que representa el nivel de "Caliente". Por ejemplo, si la temperatura es 35 C, entonces el grado de membrecía al conjunto difuso "Caliente" debe ser muy cercano a uno. Por otro lado, si la temperatura es de -20 C, entonces el grado de membrecía al conjunto difuso "Caliente" debe ser cero. Así, el valor difuso representa que tan "Caliente" está el cuarto. Algunas funciones que son usadas para crear conjuntos difusos son: la función triángulo, el trapecio, la Gaussiana, etc. |
Fuzzification |
| It is the process to convert a crisp value to a fuzzy value. As a fuzzy value may have a membership for each of its fuzzy sets, the crisp value is typically converted to a set of membership values. Es el proceso de convertir un valor nítido (crisp) a un valor difuso. Como un valor puede tener membrecía para uno de sus conjuntos difusos, el valor nítido es típicamente convertido a un conjunto de valores de membrecía. |
| Problem 1 |
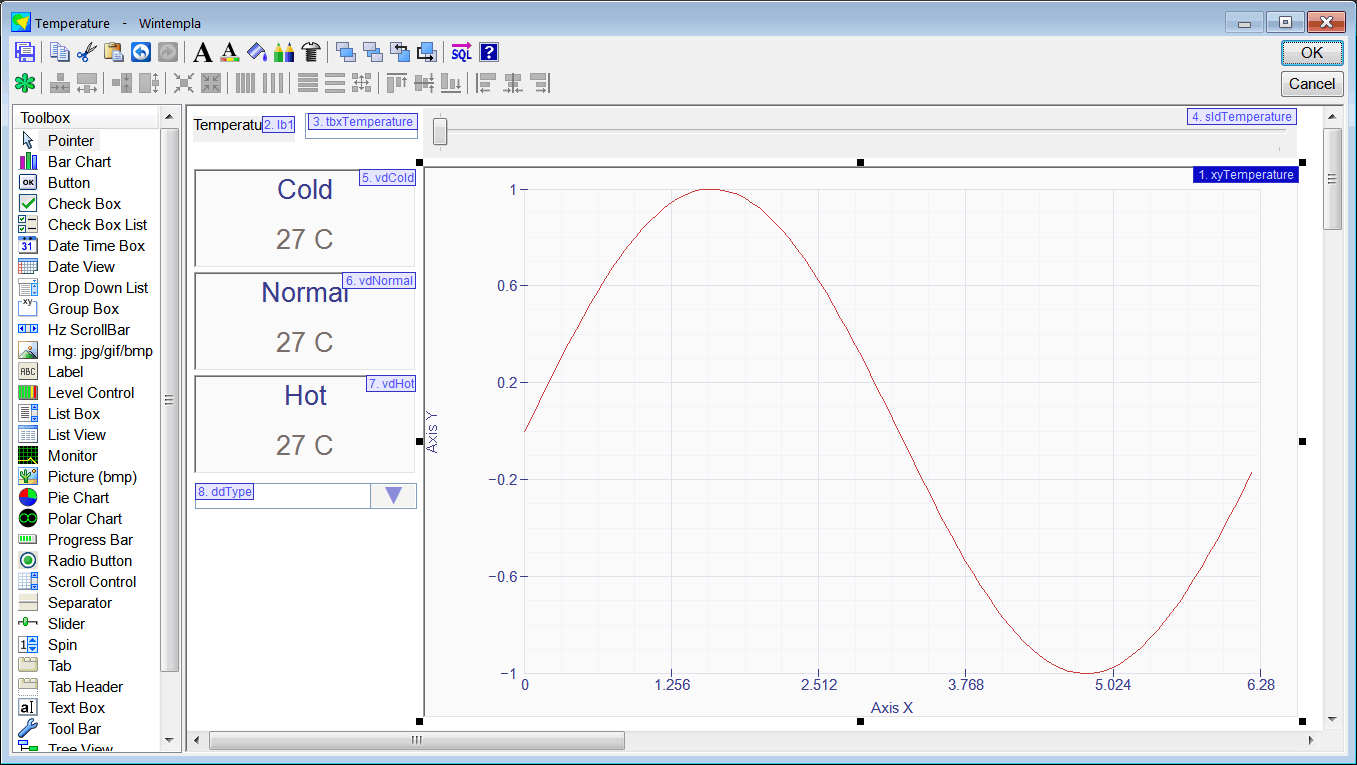
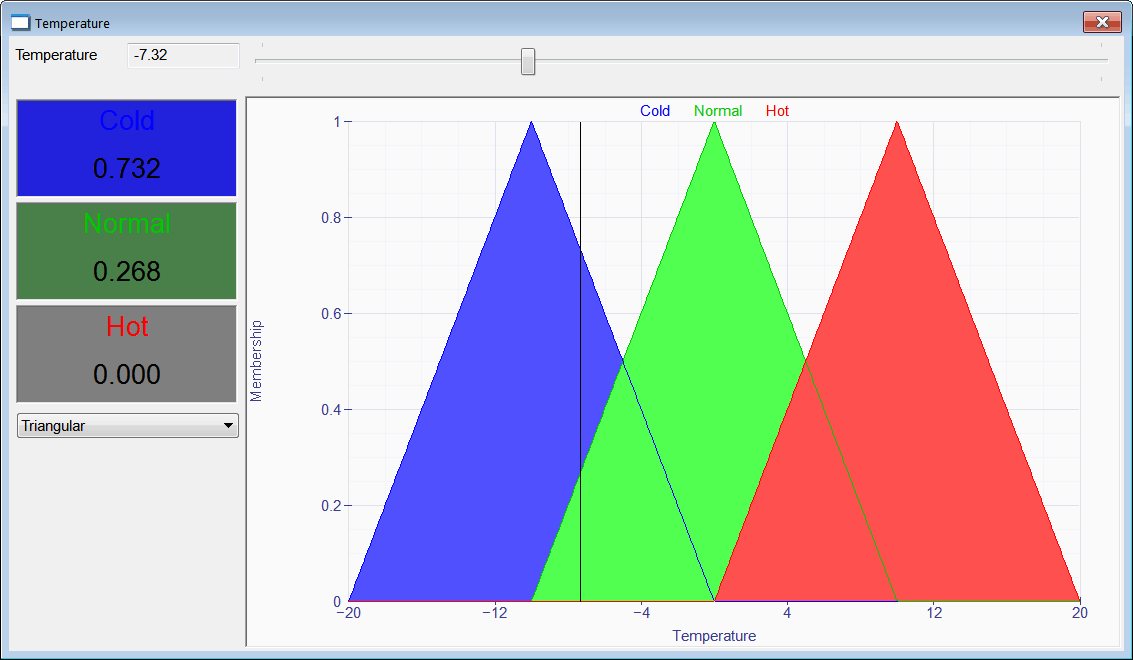
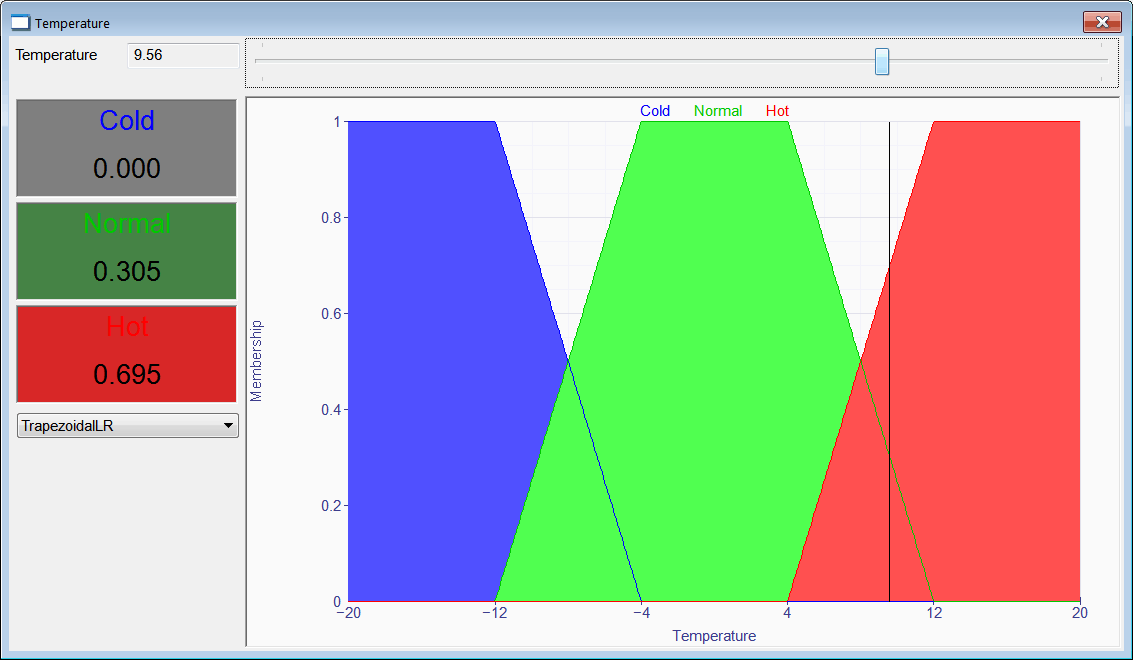
| Cree a program called Temperature with three fuzzy sets: Cold, Normal and Hot. The input crisp value is a temperature. The program must display the membership value for each of the three fuzzy sets. Insert three value displays, one drop down list, one slider, one textbox and a XyGraph as shown. Cree un programa llamado Temperature con tres conjuntos difusos: Frío, Normal y Caliente. El valor nítido es una temperatura. El programa debe mostrar el valor de membrecía para cada uno de los conjuntos difusos. Inserte tres value displays, una drop down list, un slider, una caja de texto y una XyGraph como se muestra. |
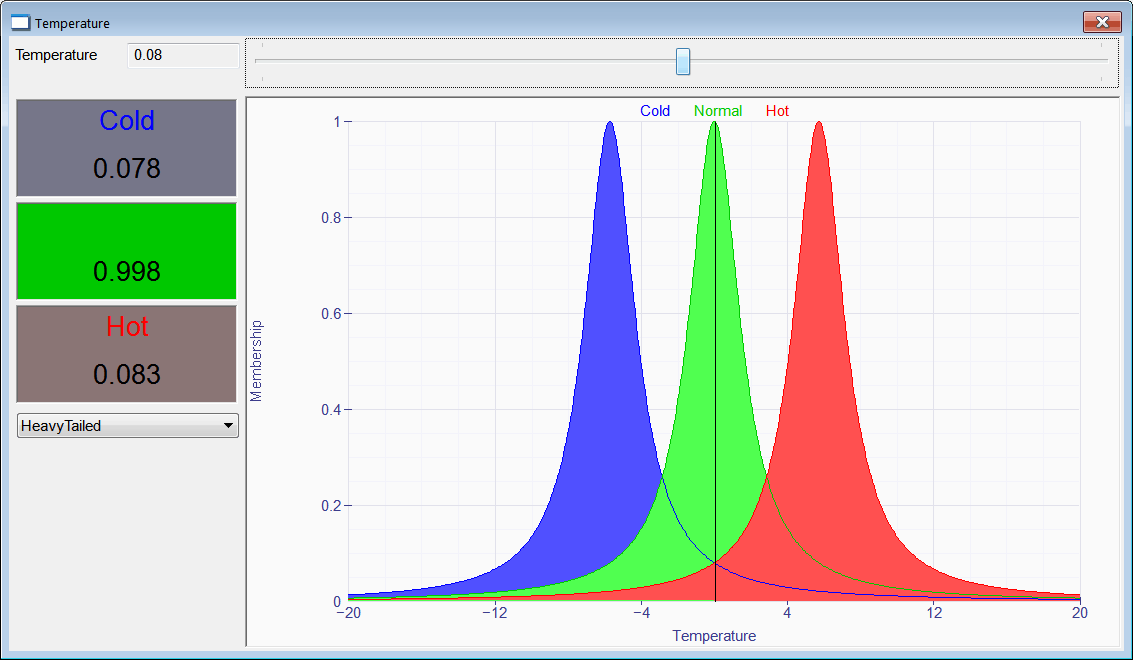
| Temperature.h |
| #pragma once //______________________________________ Temperature.h #include "Resource.h" #define SET_COUNT 3 #define POINT_COUNT 512 #define TEMPERATURE_MIN -20.0 #define TEMPERATURE_MAX 20.0 class Temperature: public Win::Dialog { public: Temperature() { } ~Temperature() { } Fuzzy::Variable inputTemperature; void UpdateGraph(); void UpdateMemberships(); void UpdateValueDisplay(Win::ValueDisplay& valueDisplay, const wchar_t* name); protected: ... }; |
| Temperature.cpp |
| ... void Temperature::Window_Open(Win::Event& e) { //________________________________________________________ xyTemperature xyTemperature.CaptionX = L"Temperature"; xyTemperature.CaptionY = L"Membership"; xyTemperature.MinX= TEMPERATURE_MIN; xyTemperature.MaxX= TEMPERATURE_MAX; xyTemperature.MinY= 0.0; xyTemperature.MaxY= 1.0; xyTemperature.Graphs.Add(POINT_COUNT); // Cold xyTemperature.Graphs.Add(POINT_COUNT); // Normal xyTemperature.Graphs.Add(POINT_COUNT); // Hot xyTemperature.Graphs.Add(2); // Temperature Vertical Line xyTemperature.Graphs[0].Color = RGB(0, 0, 255); xyTemperature.Graphs[1].Color = RGB(0, 200, 0); xyTemperature.Graphs[2].Color = RGB(255, 0, 0); //________________________________________________________ Temperature Vertical Line xyTemperature.Graphs[3].Color = RGB(0, 0, 0); xyTemperature.Graphs[3][0].x = TEMPERATURE_MIN; xyTemperature.Graphs[3][0].y = 0.0; xyTemperature.Graphs[3][1].x = TEMPERATURE_MIN; xyTemperature.Graphs[3][1].y = 1.0; //________________________________________________________ sldTemperature sldTemperature.SetRange(0, 1000); sldTemperature.Position = 0; tbxTemperature.DoubleValue = TEMPERATURE_MIN; //________________________________________________________ Value Display Text vdHot.TextColor = RGB(255, 0, 0); vdNormal.TextColor = RGB(0, 200, 0); vdCold.TextColor = RGB(0, 0, 255); //________________________________________________________ Value Display Value vdHot.ValueColor = RGB(0, 0, 0); vdNormal.ValueColor = RGB(0, 0, 0); vdCold.ValueColor = RGB(0, 0, 0); //________________________________________________________ ddType ddType.Items.Add(L"Triangular", 0); ddType.Items.Add(L"TriangularLR", 1); ddType.Items.Add(L"Trapezoidal", 2); ddType.Items.Add(L"TrapezoidalLR", 3); ddType.Items.Add(L"Sigmoidal", 4); ddType.Items.Add(L"SigmoidalLR", 5); ddType.Items.Add(L"Gaussian", 6); ddType.Items.Add(L"GaussianLR", 7); ddType.Items.Add(L"HeavyTailed", 8); ddType.Items.Add(L"HeavyTailedLR", 9); ddType.SelectedIndex = 0; //________________________________________________________ Set Initial Crisp Value inputTemperature.CrispValue = TEMPERATURE_MIN; UpdateGraph(); UpdateMemberships(); } void Temperature::UpdateGraph() { const wchar_t *names[] ={L"Cold", L"Normal", L"Hot"}; int selectedIndex = ddType.SelectedIndex; switch(selectedIndex) { case 0: inputTemperature.CreateTriangularSets(names, TEMPERATURE_MIN, TEMPERATURE_MAX, SET_COUNT); break; case 1: inputTemperature.CreateTriangularLRSets(names, TEMPERATURE_MIN, TEMPERATURE_MAX, SET_COUNT); break; case 2: inputTemperature.CreateTrapezoidalSets(names, TEMPERATURE_MIN, TEMPERATURE_MAX, SET_COUNT); break; case 3: inputTemperature.CreateTrapezoidalLRSets(names, TEMPERATURE_MIN, TEMPERATURE_MAX, SET_COUNT); break; case 4: inputTemperature.CreateSigmoidalSets(names, TEMPERATURE_MIN, TEMPERATURE_MAX, SET_COUNT); break; case 5: inputTemperature.CreateSigmoidalLRSets(names, TEMPERATURE_MIN, TEMPERATURE_MAX, SET_COUNT); break; case 6: inputTemperature.CreateGaussianSets(names, TEMPERATURE_MIN, TEMPERATURE_MAX, SET_COUNT); break; case 7: inputTemperature.CreateGaussianLRSets(names, TEMPERATURE_MIN, TEMPERATURE_MAX, SET_COUNT); break; case 8: inputTemperature.CreateHeavyTailedSets(names, TEMPERATURE_MIN, TEMPERATURE_MAX, SET_COUNT); break; case 9: inputTemperature.CreateHeavyTailedLRSets(names, TEMPERATURE_MIN, TEMPERATURE_MAX, SET_COUNT); break; } inputTemperature.GetGraph(L"Cold", POINT_COUNT, xyTemperature.Graphs[0]); inputTemperature.GetGraph(L"Normal", POINT_COUNT, xyTemperature.Graphs[1]); inputTemperature.GetGraph(L"Hot", POINT_COUNT, xyTemperature.Graphs[2]); // xyTemperature.RefreshAll(); } void Temperature::sldTemperature_Hscroll(Win::Event& e) { const int position = sldTemperature.HasPositionChanged(); if (position < 0) return; const double temperature = (position*(TEMPERATURE_MAX - TEMPERATURE_MIN)/1000.0) + TEMPERATURE_MIN; tbxTemperature.DoubleValue = temperature; //_____________________________________________________ Vertical Line xyTemperature.Graphs[3][0].x = temperature; xyTemperature.Graphs[3][1].x = temperature; xyTemperature.RefreshGraphArea(); //_____________________________________________________ Update Crisp Value inputTemperature.CrispValue = temperature; UpdateMemberships(); } void Temperature::ddType_SelChange(Win::Event& e) { UpdateGraph(); UpdateMemberships(); } void Temperature::UpdateMemberships() { UpdateValueDisplay(vdCold, L"Cold"); UpdateValueDisplay(vdNormal, L"Normal"); UpdateValueDisplay(vdHot, L"Hot"); } void Temperature::UpdateValueDisplay(Win::ValueDisplay& valueDisplay, const wchar_t* name) { const double membership = inputTemperature.GetMembership(name); wchar_t text[32]; _snwprintf_s(text, 32, _TRUNCATE, L"%.3f", membership); valueDisplay.Value = text; Sys::Color color(valueDisplay.TextColor); color.SetSaturation(membership); valueDisplay.BackColor = color.GetColor(); } |
Fuzzy logic operations |
|
Inference Rules (IF... THEN...) |
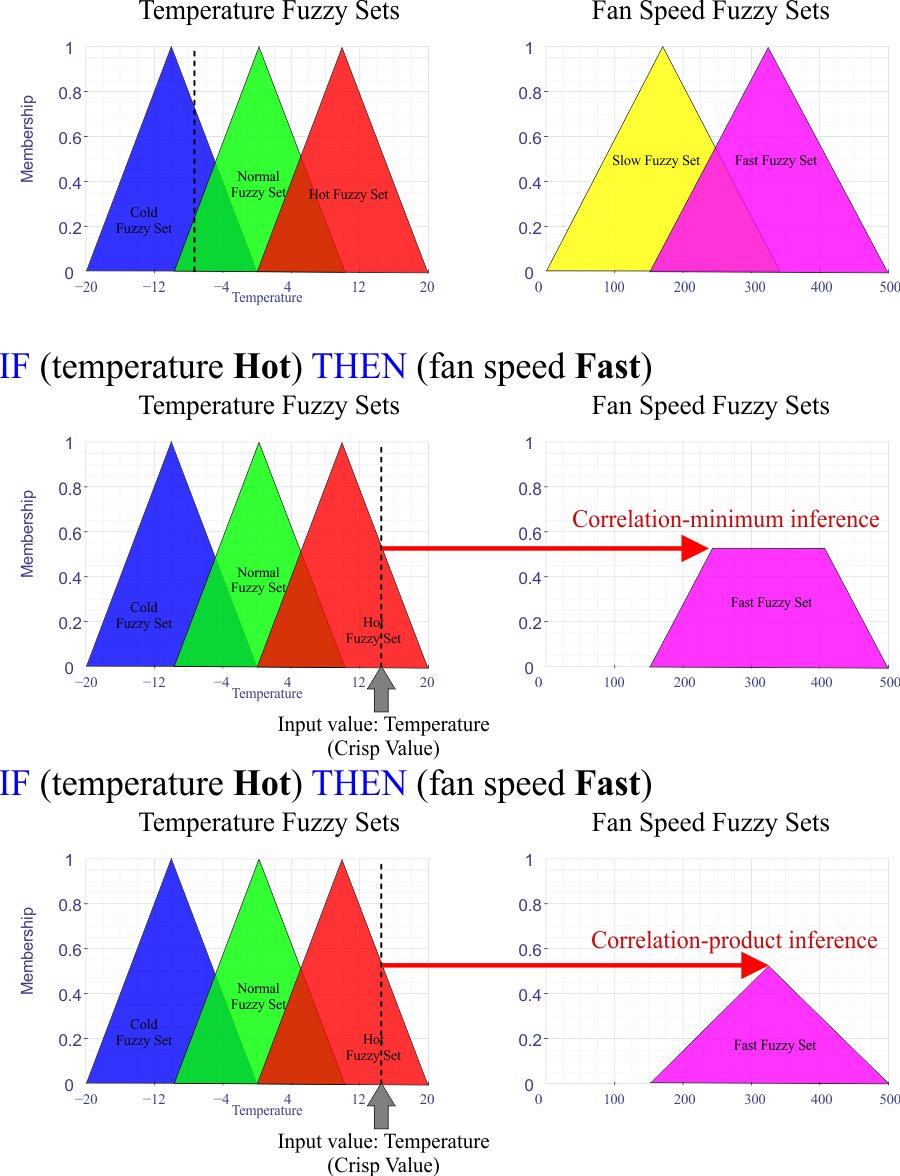
| An inference rule is an expression of the form IF ... THEN. Suppose that "Hot" is a fuzzy set thus, we can write a rule to control the speed of a fan like IF temperature Hot THEN fan speed Fast
Una regla de inferencia es una expressión de la forma IF ... THEN. Suponga que "Hot" es una conjunto difuso así, es posible escribir una regla para controlar la velocidad de un ventilador como IF temperature Hot THEN fan speed Fast
|
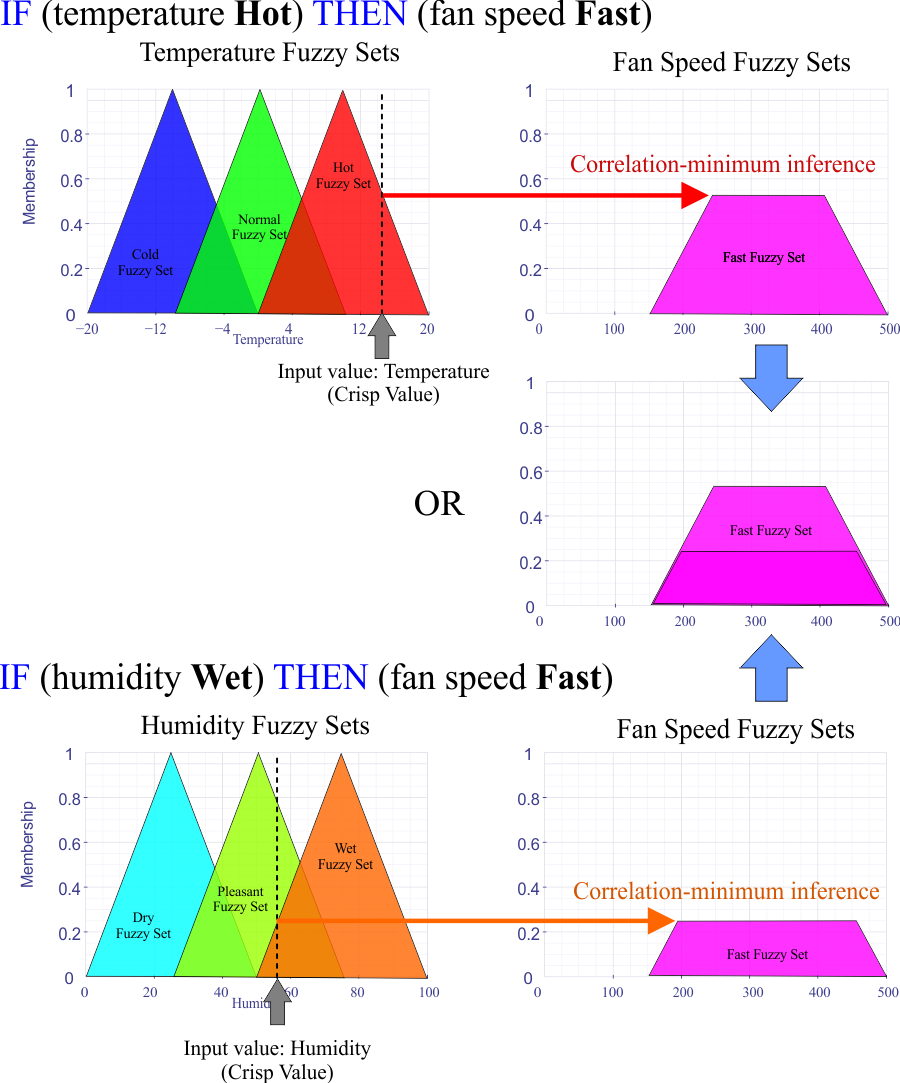
Combining Inference Rules for the same fuzzy set |
| When combining rules that affect the same output fuzzy set, the OR operation is always used as shown in the figure. In this case, the fan speed is controlled by two input variables: the temperature and the humidity. Note that both rules affect the high speed of the fan and therefore the output fuzzy sets must be combined using the OR operation (remember that the OR operation in fuzzy logic consists on finding the maximum value). Cuando se combinan reglas que afectar al mismo conjunto difuso de salida, la operación OR es siempre usada como se muestra en la figura. En este caso, la velocidad del ventilador está controlada por dos variables de entrada: la temperatura y la humedad. Note que ambas reglas afectan la velocidad alta del ventilador y por lo tanto los conjuntos difusos de salida debe ser combinados usando la operación OR (recuerde que la operación OR en lógica difusa consiste en encontrar el valor máximo). |
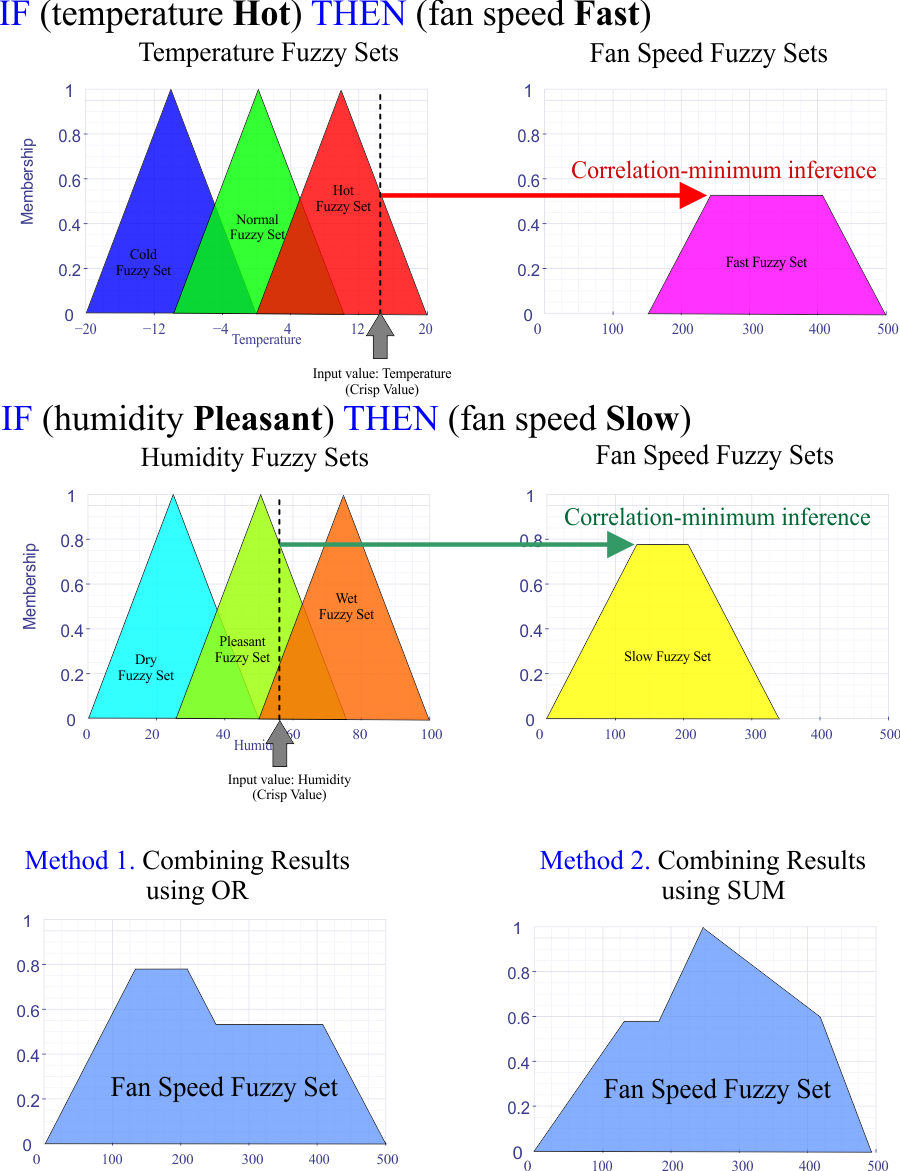
Combining Inference Rules |
In most fuzzy logic application, you will need a set of rules and you need to combine all rules to produce one single output fuzzy set. There are two methods to combine rules:
En la mayoría de las aplicaciones lógica difusa, usted necesitará un conjunto de reglas y usted necesita combinar todas las reglas para producir un solo conjunto difuso. Hay dos métodos para combinar las reglas:
|
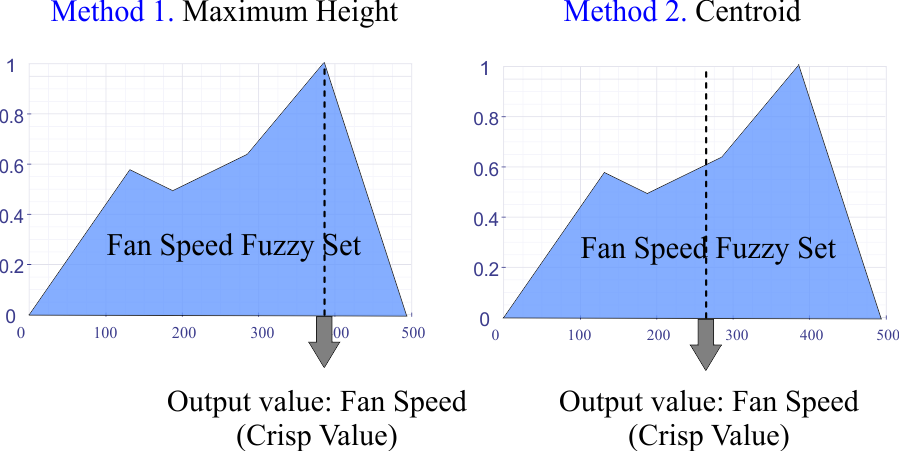
Defuzzification |
In some applications, it is necessary to convert the output fuzzy value to a crisp value. There are two typical methods to do this as shown in the figure.
En algunas aplicaciones, es necesario convertir el valor difuso de salida a un valor nítido. Hay dos métodos típicos para hacer esto como se muestra en la figura.
|
| Problem 2 |
| Create a Wintempla Window application called TempInfe to test inference rules using fuzzy logic. Using the following rules: IF temperature Hot THEN fan speed Fast IF temperature Normal OR temperature Cold THEN fan speed Slow Cree una aplicación de Ventana de Wintempla llamada TempInfe para probar las reglas de inferencia usando lógica difusa. Usando las reglas mostradas. |
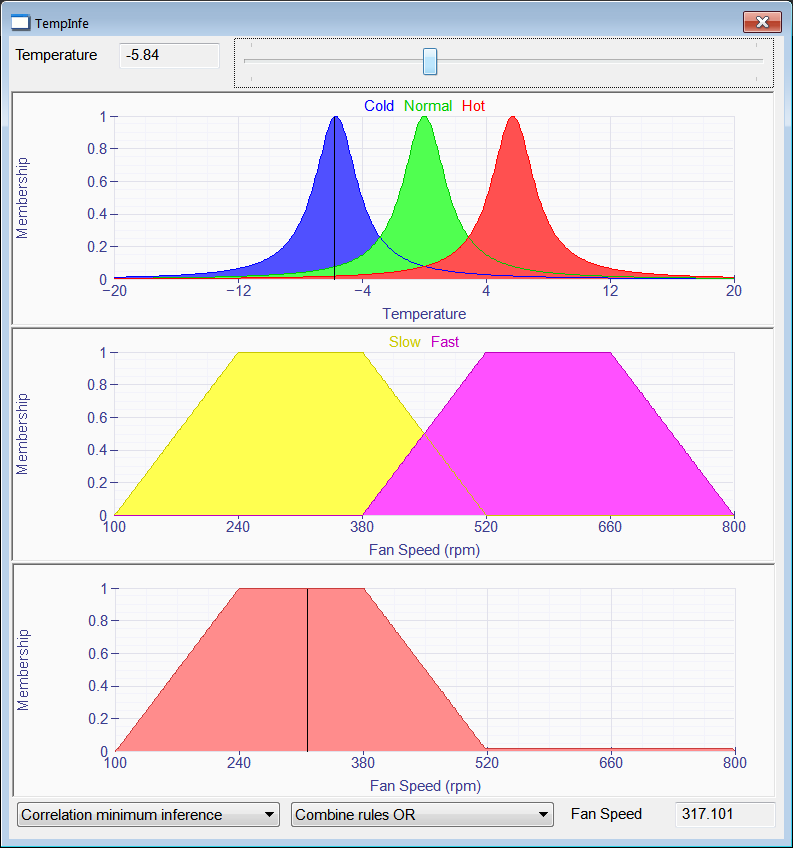
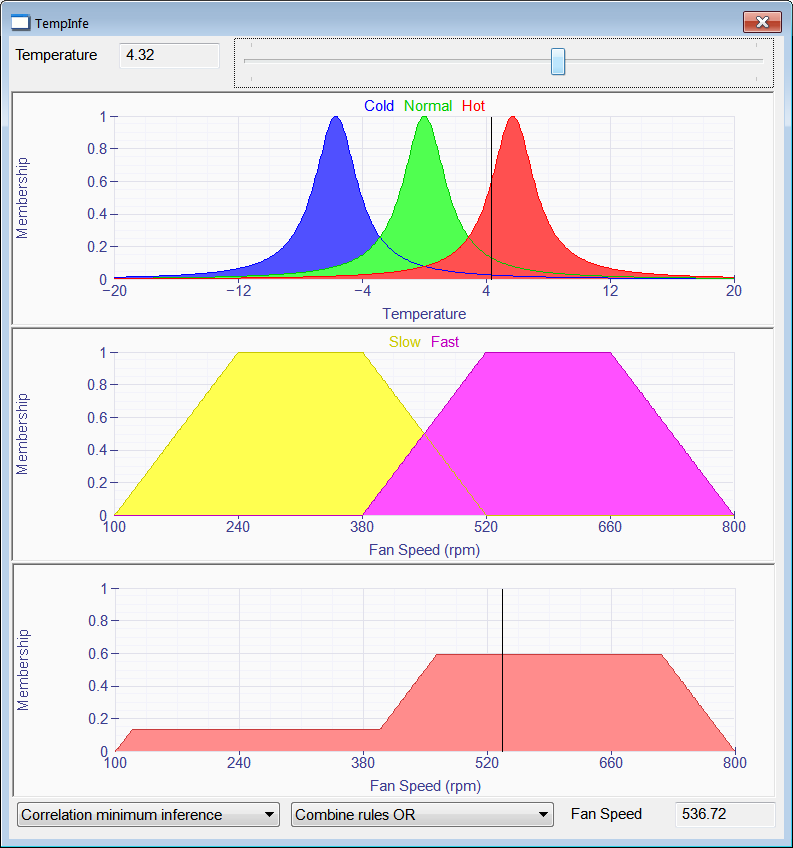
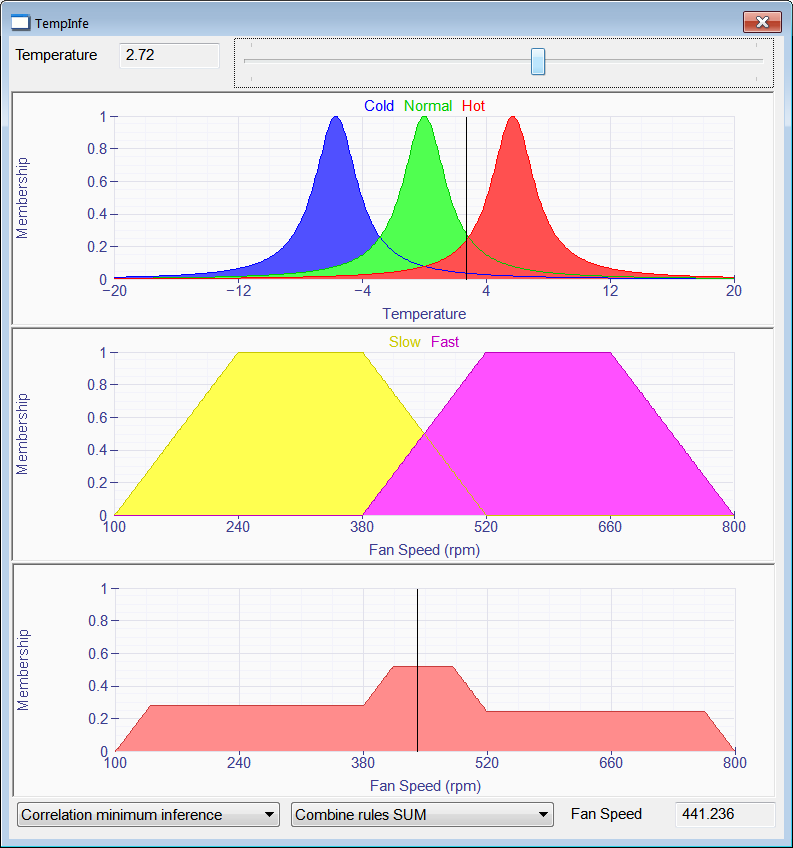
| TempInfe.h |
| #pragma once //______________________________________ TempInfe.h #include "Resource.h" #define POINT_COUNT 512 #define TEMPERATURE_MIN -20.0 #define TEMPERATURE_MAX 20.0 // #define FAN_SPEED_MIN 100 #define FAN_SPEEN_MAX 800 class TempInfe: public Win::Dialog { public: TempInfe() { } ~TempInfe() { } void Update(); Fuzzy::Variable temperature; Fuzzy::Variable fanSpeed; ... }; |
| TempInfe.cpp |
| ... void TempInfe::Window_Open(Win::Event& e) { //_______________________________________________________________ Fuzzy Variable for the temperature temperature.CrispValue = TEMPERATURE_MIN; const wchar_t *temperatureNames[] ={L"Cold", L"Normal", L"Hot"}; temperature.CreateHeavyTailedSets(temperatureNames, TEMPERATURE_MIN, TEMPERATURE_MAX, 3); //_______________________________________________________________ Fuzzy Variable for the fan speed fanSpeed.CrispValue = FAN_SPEED_MIN; const wchar_t *fanSpeedNames[] ={L"Slow", L"Fast"}; fanSpeed.CreateTrapezoidalSets(fanSpeedNames, FAN_SPEED_MIN, FAN_SPEEN_MAX, 2); //________________________________________________________ xyTemperature xyTemperature.CaptionX = L"Temperature"; xyTemperature.CaptionY = L"Membership"; xyTemperature.MinX= TEMPERATURE_MIN; xyTemperature.MaxX= TEMPERATURE_MAX; xyTemperature.MinY= 0.0; xyTemperature.MaxY= 1.0; xyTemperature.Graphs.Add(POINT_COUNT); // Cold xyTemperature.Graphs.Add(POINT_COUNT); // Normal xyTemperature.Graphs.Add(POINT_COUNT); // Hot xyTemperature.Graphs.Add(2); // Temperature Vertical Line xyTemperature.Graphs[0].Color = RGB(0, 0, 255); xyTemperature.Graphs[1].Color = RGB(0, 200, 0); xyTemperature.Graphs[2].Color = RGB(255, 0, 0); temperature.GetGraph(L"Cold", POINT_COUNT, xyTemperature.Graphs[0]); temperature.GetGraph(L"Normal", POINT_COUNT, xyTemperature.Graphs[1]); temperature.GetGraph(L"Hot", POINT_COUNT, xyTemperature.Graphs[2]); // xyTemperature.RefreshAll(); //________________________________________________________ Temperature Vertical Line xyTemperature.Graphs[3].Color = RGB(0, 0, 0); xyTemperature.Graphs[3][0].x = TEMPERATURE_MIN; xyTemperature.Graphs[3][0].y = 0.0; xyTemperature.Graphs[3][1].x = TEMPERATURE_MIN; xyTemperature.Graphs[3][1].y = 1.0; //________________________________________________________ sldTemperature sldTemperature.SetRange(0, 1000); sldTemperature.Position = 0; tbxTemperature.DoubleValue = TEMPERATURE_MIN; //________________________________________________________ xyFanSpeed xyFanSpeed.CaptionX = L"Fan Speed (rpm)"; xyFanSpeed.CaptionY = L"Membership"; xyFanSpeed.MinX= FAN_SPEED_MIN; xyFanSpeed.MaxX= FAN_SPEEN_MAX; xyFanSpeed.MinY= 0.0; xyFanSpeed.MaxY= 1.0; xyFanSpeed.Graphs.Add(POINT_COUNT); // Slow xyFanSpeed.Graphs.Add(POINT_COUNT); // Fast xyFanSpeed.Graphs.Add(2); // Temperature Vertical Line xyFanSpeed.Graphs[0].Color = RGB(200, 200, 0); xyFanSpeed.Graphs[1].Color = RGB(190, 0, 190); xyFanSpeed.Graphs[2].Color = RGB(0, 0, 0); fanSpeed.GetGraph(L"Slow", POINT_COUNT, xyFanSpeed.Graphs[0]); fanSpeed.GetGraph(L"Fast", POINT_COUNT, xyFanSpeed.Graphs[1]); xyFanSpeed.RefreshAll(); //________________________________________________________ xyOutput xyOutput.CaptionX = L"Fan Speed (rpm)"; xyOutput.CaptionY = L"Membership"; xyOutput.MinX= FAN_SPEED_MIN; xyOutput.MaxX= FAN_SPEEN_MAX; xyOutput.MinY= 0.0; xyOutput.MaxY= 1.0; xyOutput.Graphs.Add(POINT_COUNT); //_____________________________ Fan Speed Vertical Line xyOutput.Graphs.Add(2); xyOutput.Graphs[1].Color = RGB(0, 0, 0); xyOutput.Graphs[1][0].x = FAN_SPEED_MIN; xyOutput.Graphs[1][0].y = 0.0; xyOutput.Graphs[1][1].x = FAN_SPEED_MIN; xyOutput.Graphs[1][1].y = 1.0; xyOutput.RefreshAll(); //________________________________________________________ ddInference ddInference.Items.Add(L"Correlation minimum inference", FUZZY_CORRELATION_MINIMUM_INFERENCE); ddInference.Items.Add(L"Correlation product inference", FUZZY_CORRELATION_PRODUCT_INFERENCE); ddInference.SelectedIndex = 0; //________________________________________________________ ddCombineRules ddCombineRules.Items.Add(L"Combine rules OR", FUZZY_COMBINE_RULES_OR); ddCombineRules.Items.Add(L"Combine rules SUM", FUZZY_COMBINE_RULES_SUM); ddCombineRules.SelectedIndex = 0; } void TempInfe::sldTemperature_Hscroll(Win::Event& e) { const int position = sldTemperature.HasPositionChanged(); if (position < 0) return; tbxTemperature.DoubleValue = (position*(TEMPERATURE_MAX - TEMPERATURE_MIN)/1000.0) + TEMPERATURE_MIN; Update(); } void TempInfe::ddInference_SelChange(Win::Event& e) { Update(); } void TempInfe::ddCombineRules_SelChange(Win::Event& e) { Update(); } void TempInfe::Update() { const double new_temperature = tbxTemperature.DoubleValue; LPARAM data; if (ddInference.GetSelectedData(data) == true) fanSpeed.correlationInference = (int)data; if (ddCombineRules.GetSelectedData(data) == true) fanSpeed.combineRulesMethod = (int)data; //_____________________________________________________ 1. Vertical Line for Temperature xyTemperature.Graphs[3][0].x = new_temperature; xyTemperature.Graphs[3][1].x = new_temperature; xyTemperature.RefreshGraphArea(); //_____________________________________________________ 2. Update Crisp Value temperature.CrispValue = new_temperature; //_____________________________________________________ 3. Apply Inference Rules fanSpeed[L"Slow"].IF(temperature[L"Normal"] || temperature[L"Cold"]); fanSpeed[L"Fast"].IF(temperature[L"Hot"]); //_____________________________________________________ 4. Display Output Variable: fanSpeed fanSpeed.GetOutputGraph(POINT_COUNT, xyOutput.Graphs[0]); //_____________________________________________________ 5. Defuzzify const double new_fanSpeed = fanSpeed.CrispValue; tbxFanSpeed.DoubleValue = new_fanSpeed; xyOutput.Graphs[1][0].x = new_fanSpeed; xyOutput.Graphs[1][1].x = new_fanSpeed; xyOutput.RefreshAll(); } |